 |
 |
 |
 |
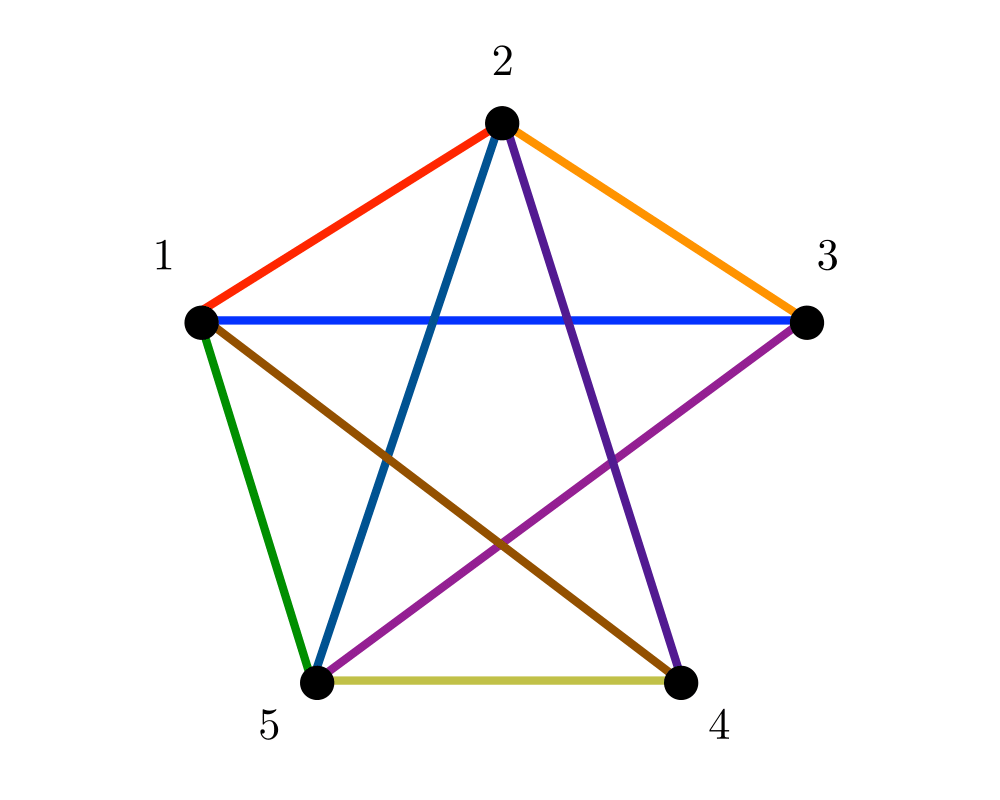
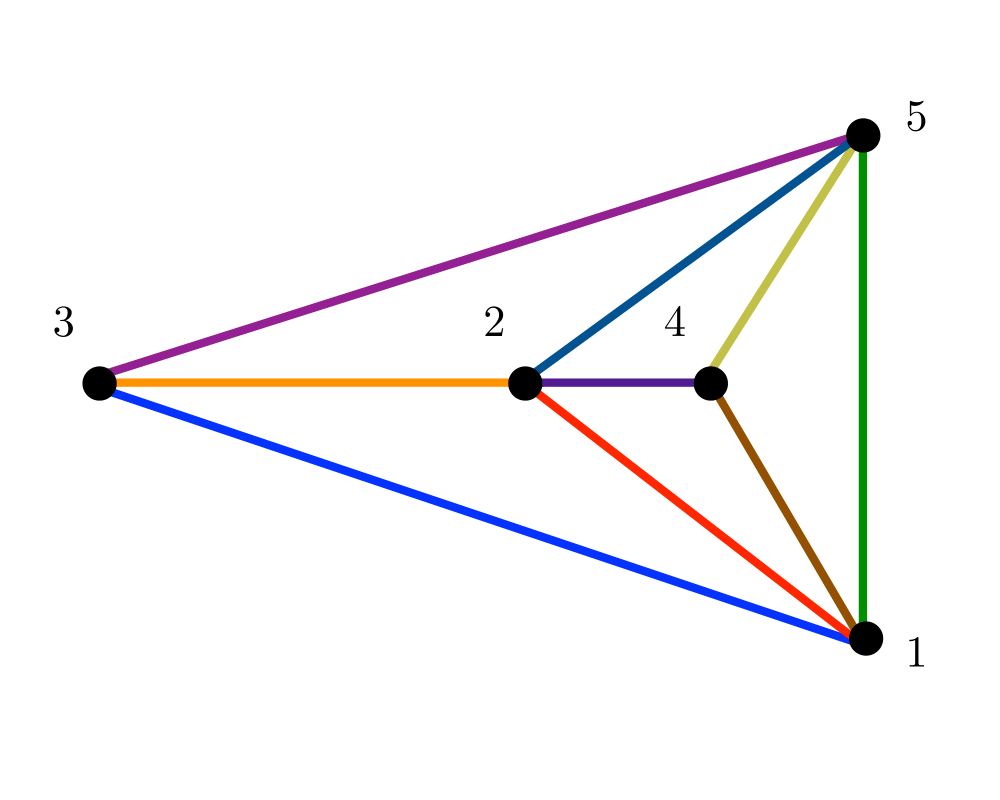
Input Description: A graph \(G\).
Problem: Can \(G\) be drawn in the plane such that no two edges cross? If so, produce such a drawing.
Excerpt from The Algorithm Design Manual: Planar drawings (or embeddings) make it easy to understand the structure of a given graph by eliminating crossing edges, which are often confused as additional vertices. Graphs arising in many applications, such as road networks or printed circuit boards, are naturally planar because they are defined by surface structures.
Planar graphs have a variety of nice properties, which can be exploited to yield faster algorithms for many problems on planar graphs. Perhaps the most important property is that every planar graph is sparse. Euler's formula shows that for planar graph \(G=(V,E)\), \(|E| \leq 3 |V| - 6\), so every planar graph contains a linear number of edges, and further, every planar graph must contain a vertex of degree at most \(5\). Since every subgraph of a planar graph is planar, this means that there is always a sequence of low-degree vertices whose deletion from \(G\) eventually leaves the empty graph.
It is useful to distinguish the problem of planarity testing (does a graph have a planar drawing) from constructing planar embeddings (actually finding the drawing), although both can be done in linear time. Surprisingly, many efficient algorithms for planar graphs do not make use of the drawing but use the low-degree deletion sequence described above.
| LEDA (rating 10) |
JGraphEd (rating 9) |
| GOBLIN (rating 9) |
GRASP (rating 8) |
| GraphEd (rating 7) |
planarity (rating 6) |
| Combinatorica (rating 2) |
 Planar Graph Drawing by T. Nishizeki and S. Rahman Planar Graph Drawing by T. Nishizeki and S. Rahman |
 Graph Drawing: Algorithms for the Visualization of Graphs by Giuseppe Di Battista, Peter Eades, Roberto Tamassia, and Ionnis G. Tollis Graph Drawing: Algorithms for the Visualization of Graphs by Giuseppe Di Battista, Peter Eades, Roberto Tamassia, and Ionnis G. Tollis |
  Drawing Graphs Nicely |
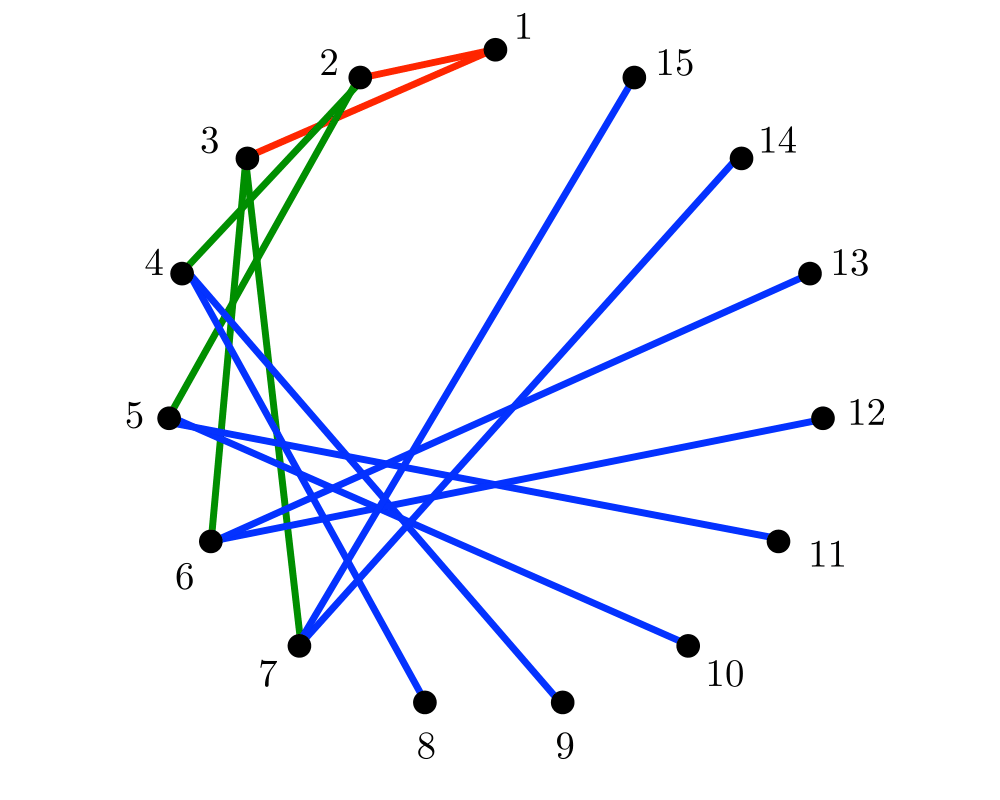 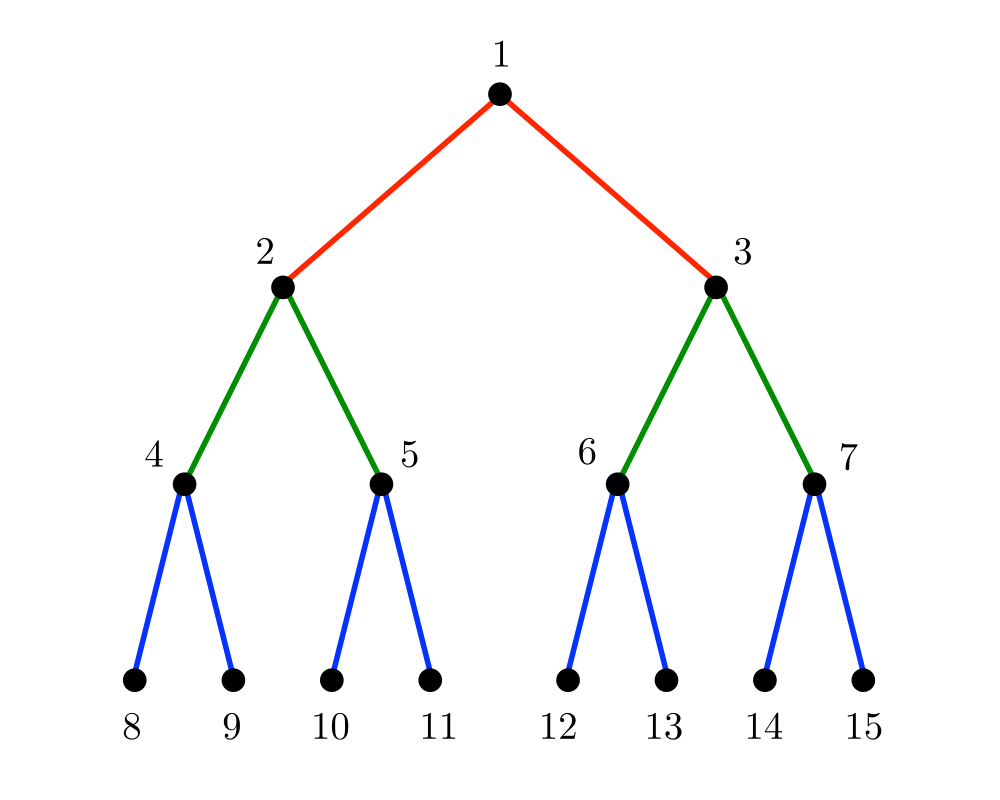 Drawing Trees |
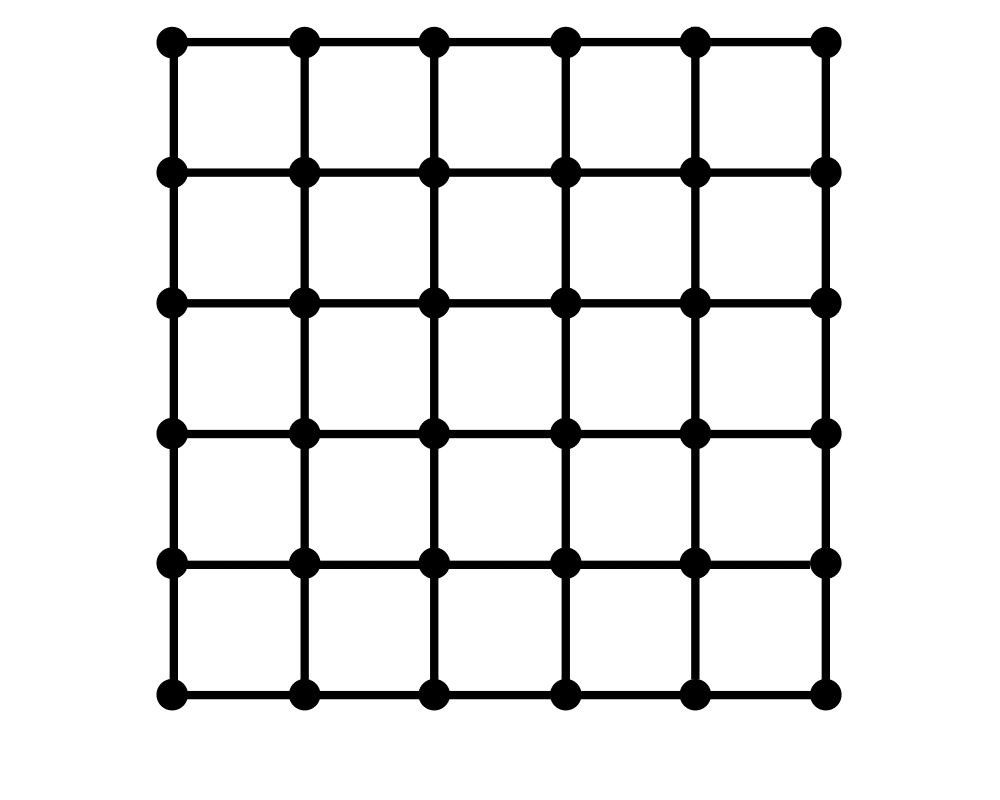 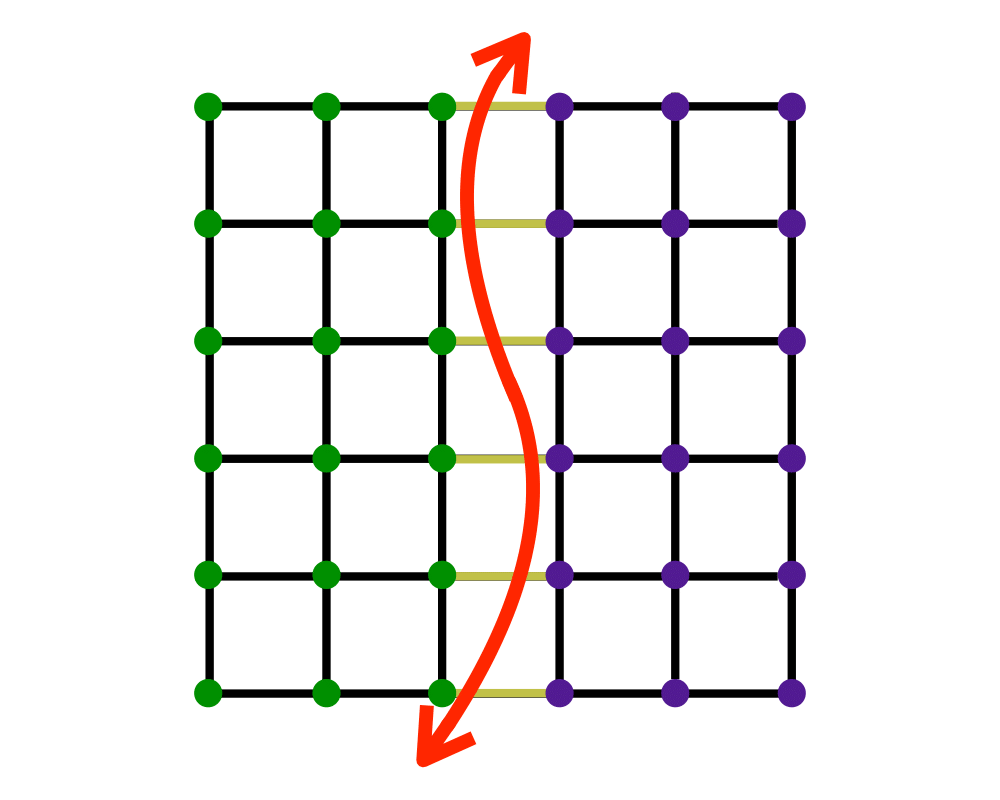 Graph Partition |
As an Amazon affiliate, I earn from qualifying purchases if you buy from links on this website.