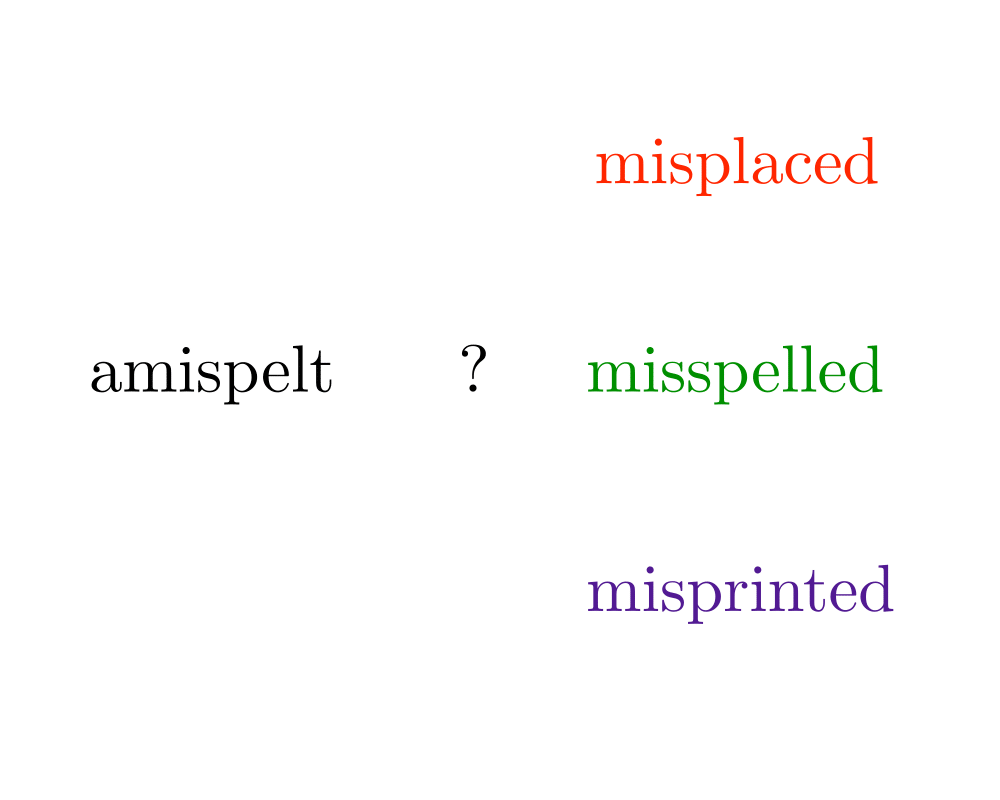 |
 |
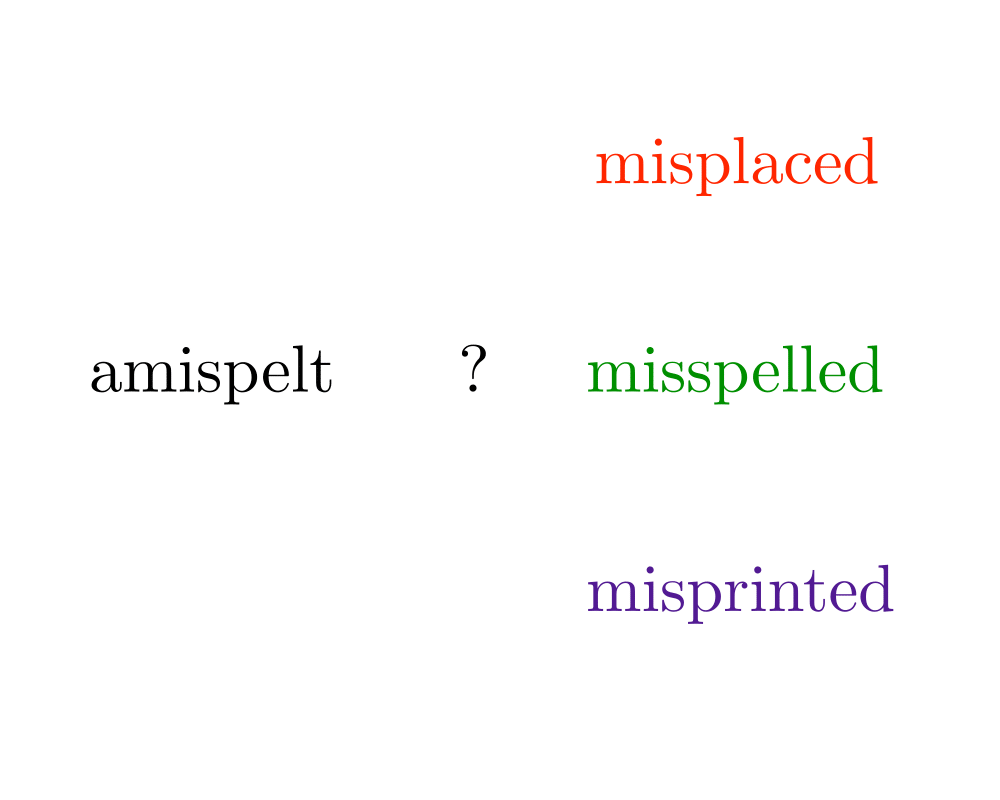 |
 |
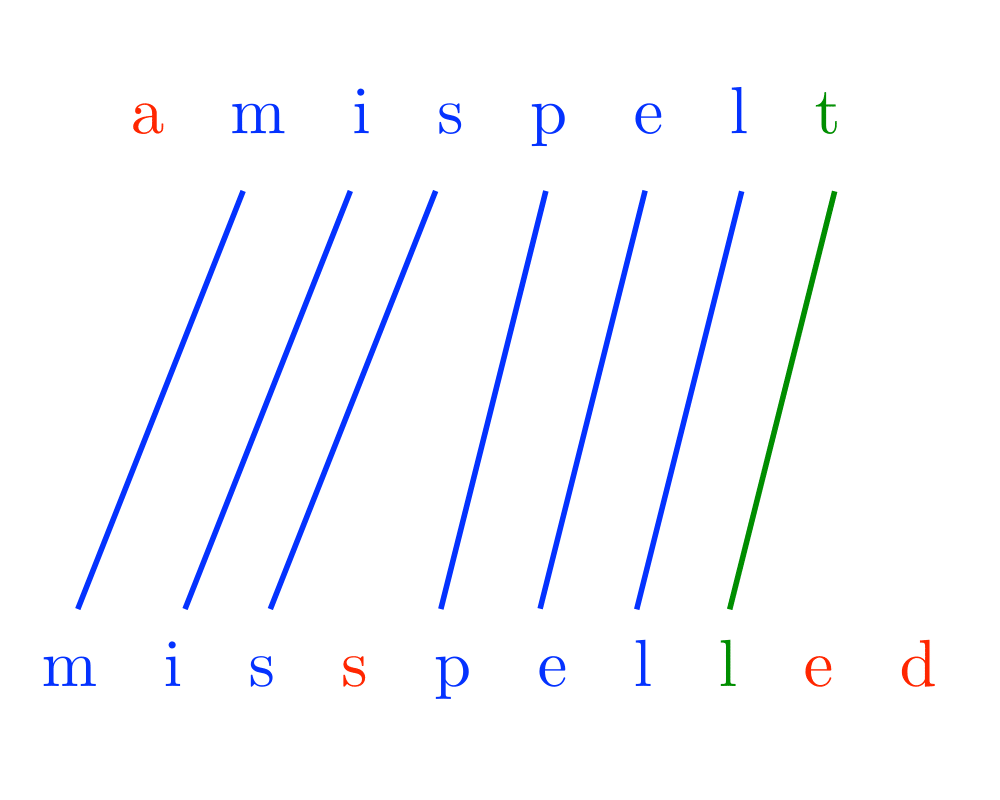
Input Description: A text string \(t\) and a pattern string \(p\). An edit cost bound \(k\).
Problem: Does there exist an alignment between \(t\) and \(p\) with edit cost at most \(k\), ie. can we transform part of \(t\) to \(p\) using at most \(k\) additions, deletions, and substitutions.
Excerpt from The Algorithm Design Manual: Approximate string matching is fundamental to text processing, because we live in an error-prone world. Any spelling correction program must be able to identify the closest match for any text string not found in a dictionary. Genbank has become a fundamental tool for molecular biology by supporting homology (similarity) searches on DNA sequences. Suppose you were to sequence a new gene in man, and you discovered that it is similar to the hemoglobin gene in rats. It is likely that this new gene also produces hemoglobin, and any differences are the result of genetic mutations during evolution.
| TRE (rating 9) |
fuzzywuzzy (rating 8) |
| agrep (rating 7) |
matchr (rating 7) |
| amatch (rating 7) |
HT/DIG (rating 5) |
| Handbook of Algorithms and Data Structures (rating 2) |