 |
 |
 |
 |
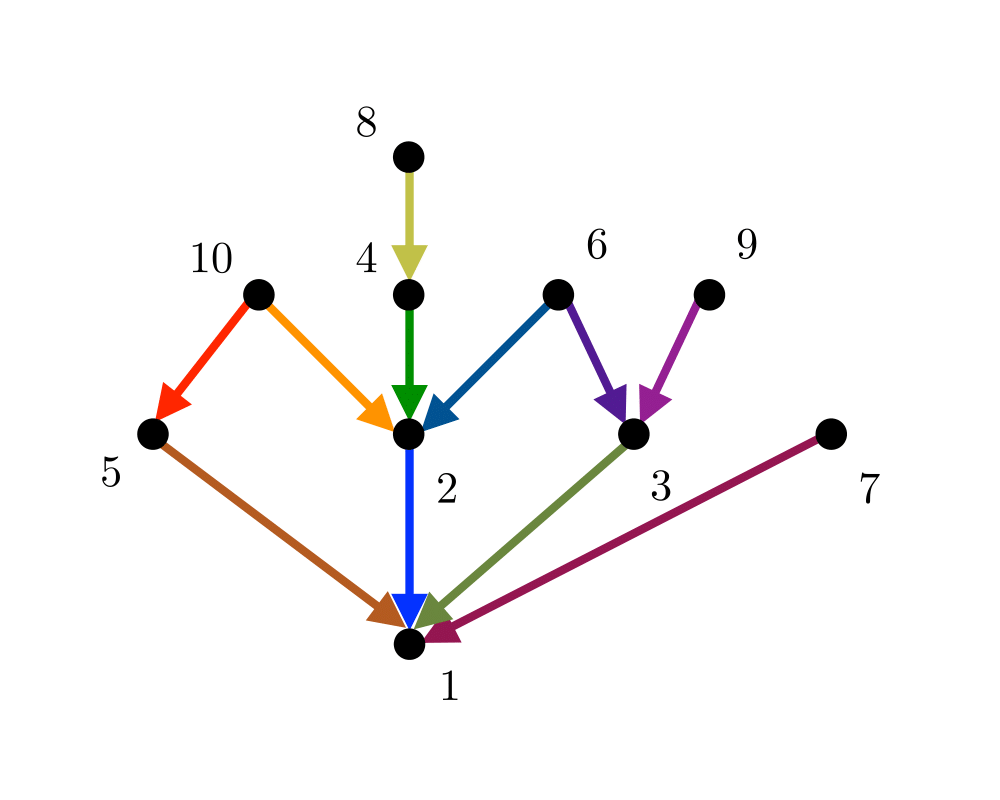
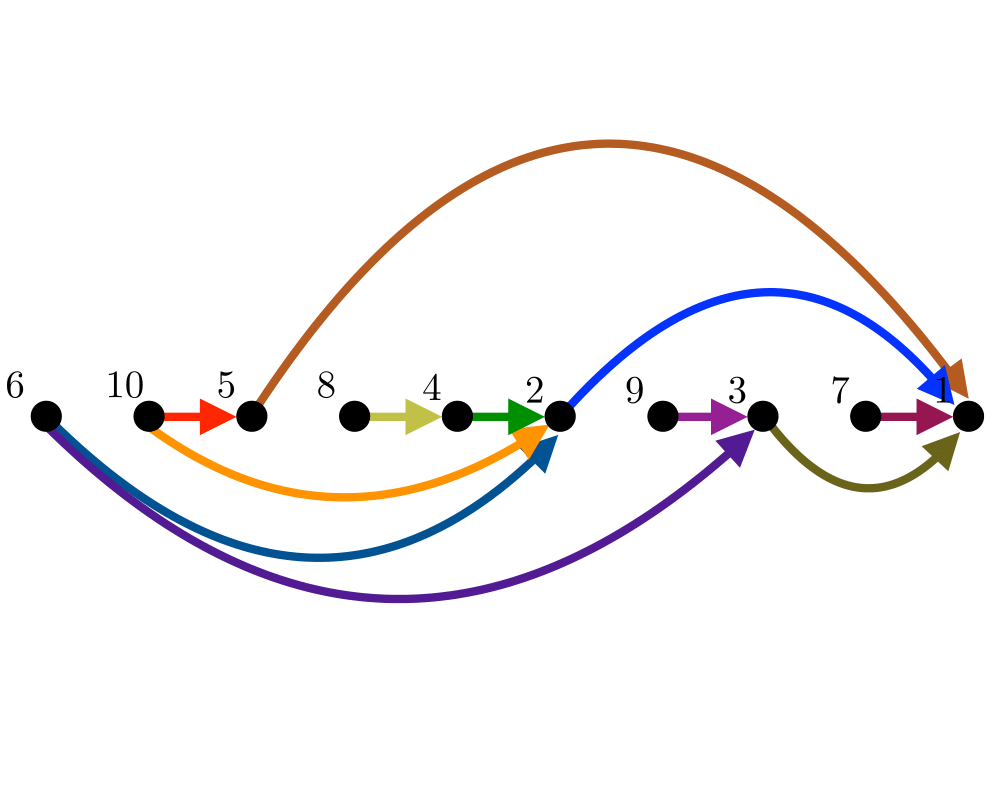
Input Description: A directed, acyclic graph \(G=(V,E)\) (also known as a partial order or poset).
Problem: Find a linear ordering of the vertices of \(V\) such that for each edge \((i,j) \in E\), vertex \(i\) is to the left of vertex \(j\).
Excerpt from The Algorithm Design Manual: Topological sorting arises as a natural subproblem in most algorithms on directed acyclic graphs. Topological sorting orders the vertices and edges of a DAG in a simple and consistent way and hence plays the same role for DAGs that depth-first search does for general graphs.
Topological sorting can be used to schedule tasks under precedence constraints. Suppose we have a set of tasks to do, but certain tasks have to be performed before other tasks. These precedence constraints form a directed acyclic graph, and any topological sort (also known as a linear extension) defines an order to do these tasks such that each is performed only after all of its constraints are satisfied.