 |
 |
 |
 |
Input Description: A universe of objects \(U = \{ u_1,...,u_n\}\), and a collection of subsets \(S_1,...,S_m\), \(S_i \subset U\).
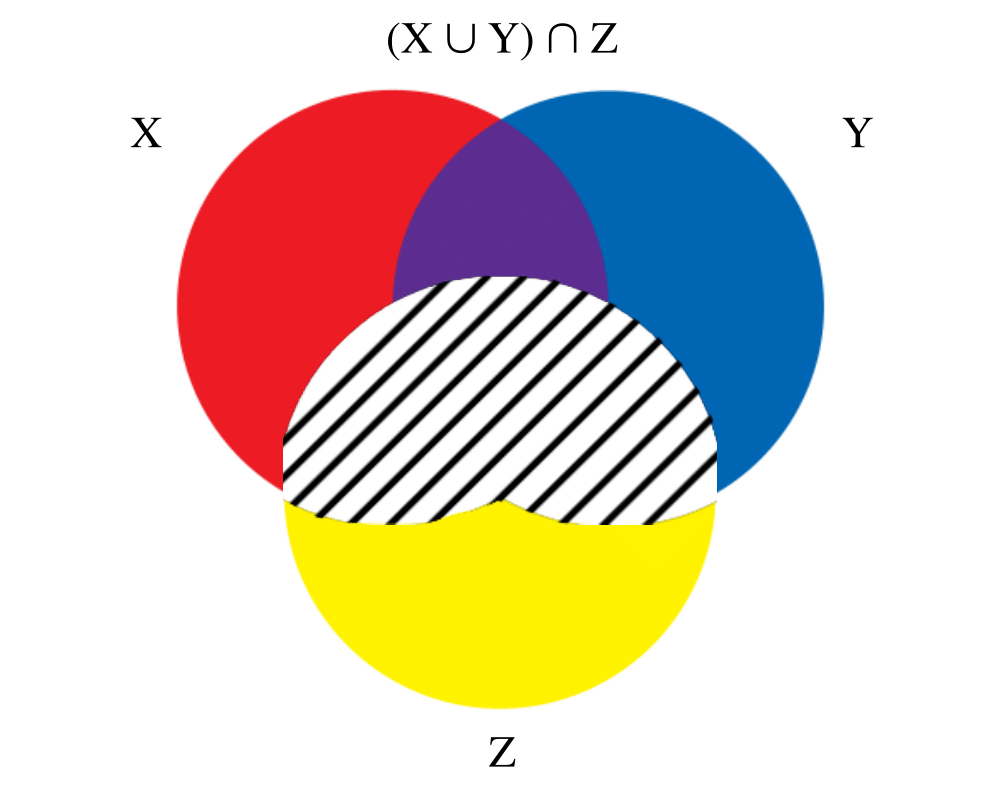
Problem: Represent each subset so as to efficiently (1) test whether \(u_i \in S_j\), (2) find the union or intersection of \(S_i\) and \(S_j\), (3) insert or delete members of \(S_i\).
Excerpt from The Algorithm Design Manual: We distinguish sets from two other kinds of objects: strings and dictionaries. If there is no fixed-size universal set, a collection of objects is best thought of as a dictionary. If the order does matter in a subset, i.e. if {A,B,C} is not the same as {B,C,A}, then your structure is more profitably thought of as a string.
When each subset has cardinality exactly two, they form edges in a graph whose vertices are the universal set. A system of subsets with no restrictions on the cardinality of its members is called a hypergraph. It often can be profitable to consider whether your problem has a graph-theoretical analogy, like connected components or shortest path in a hypergraph.
Your primary alternatives for representing arbitrary systems of subsets are:
 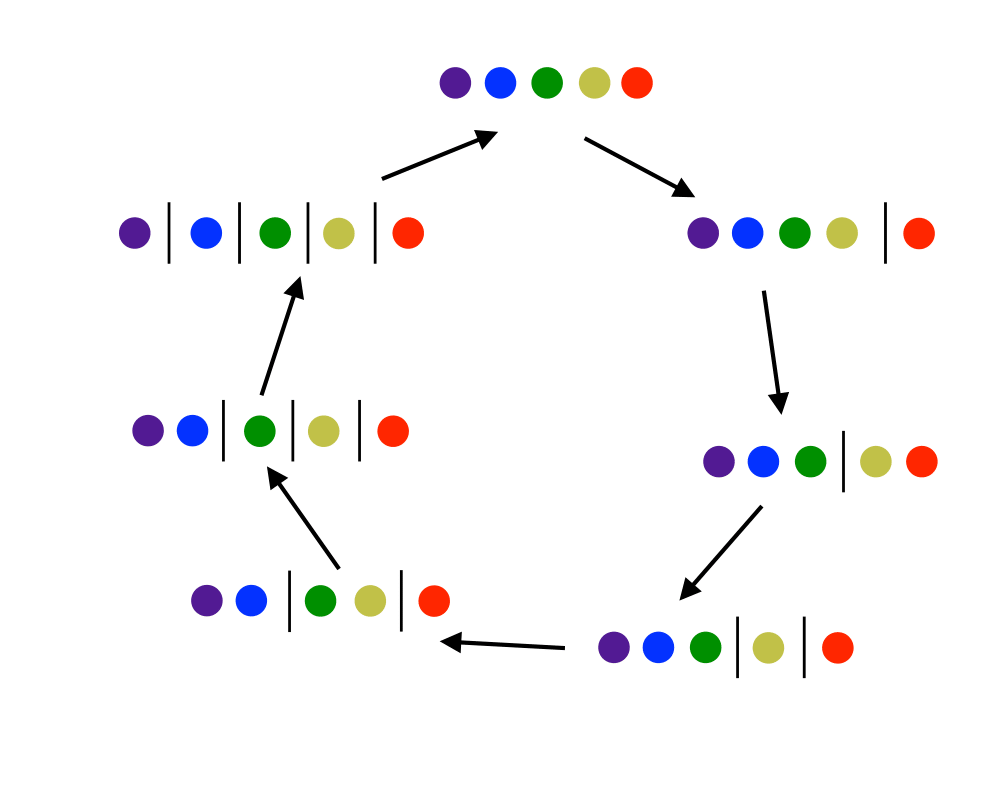 Generating Partitions |
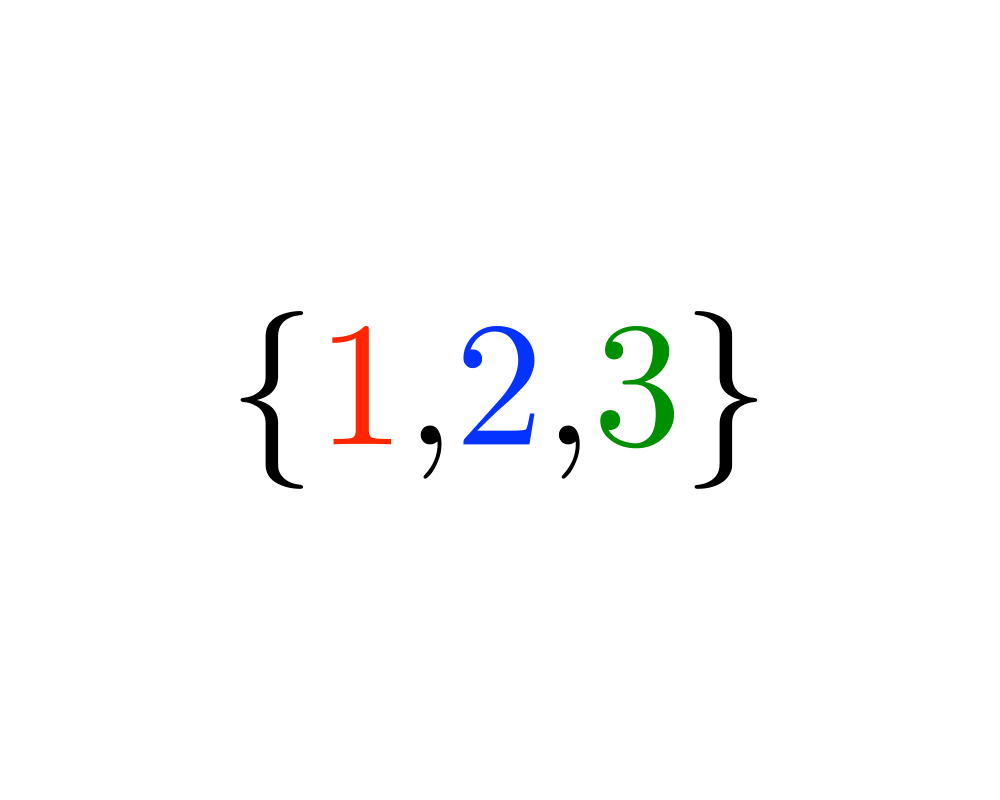 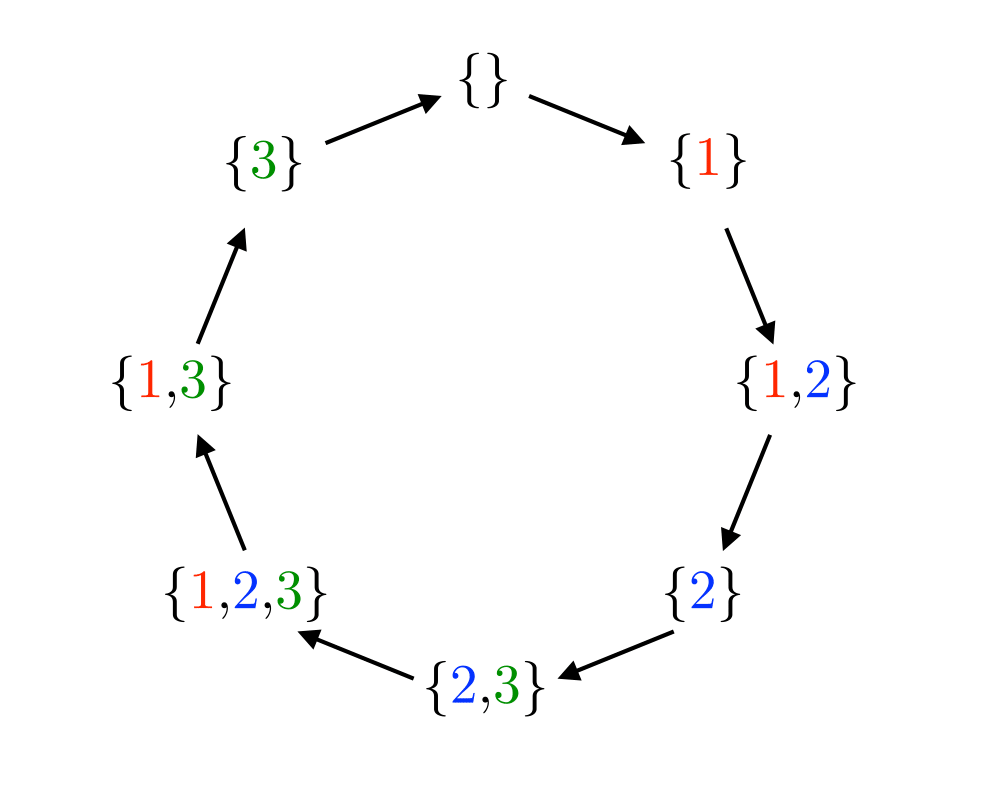 Generating Subsets |
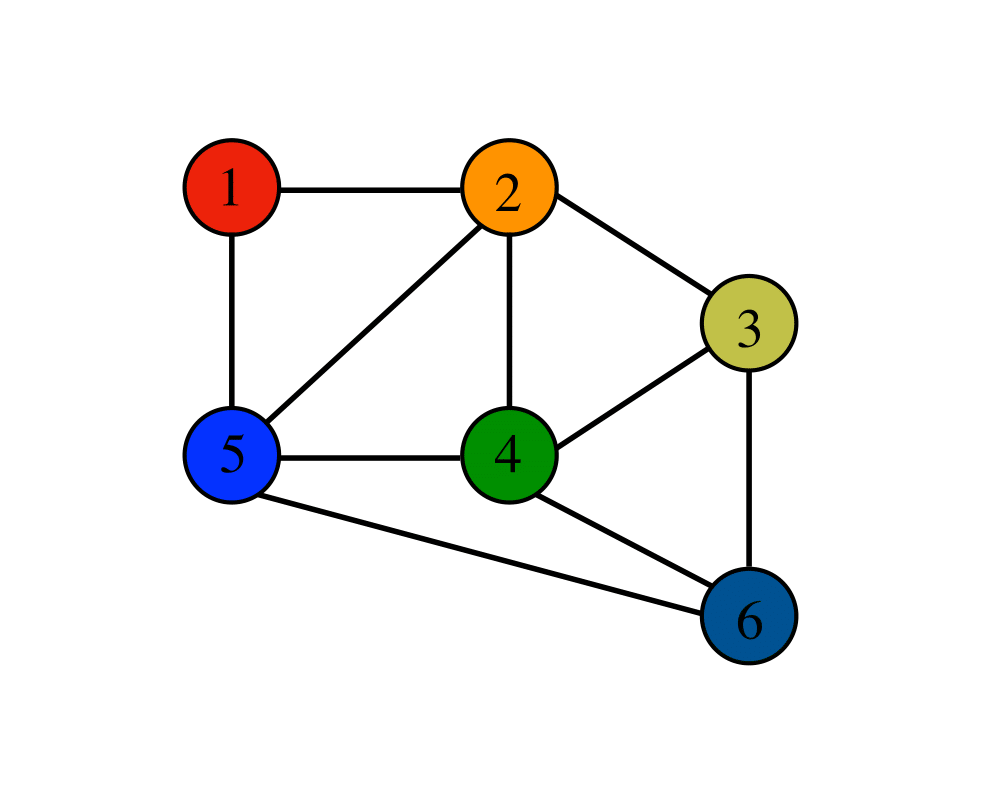 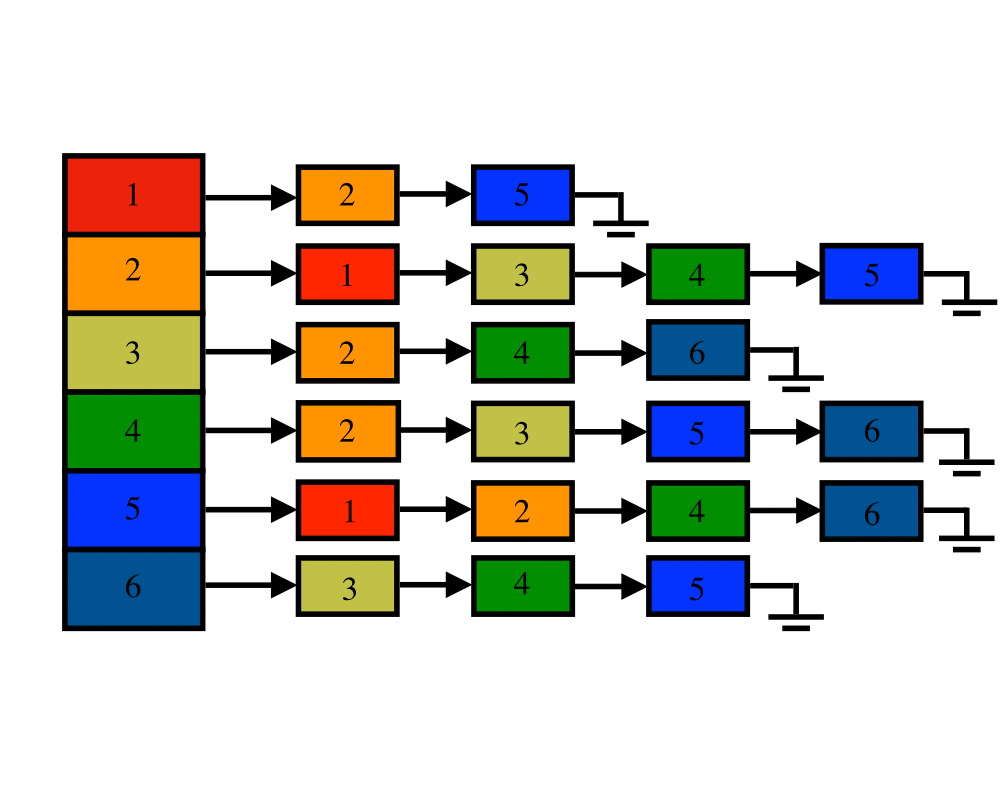 Graph Data Structures |
 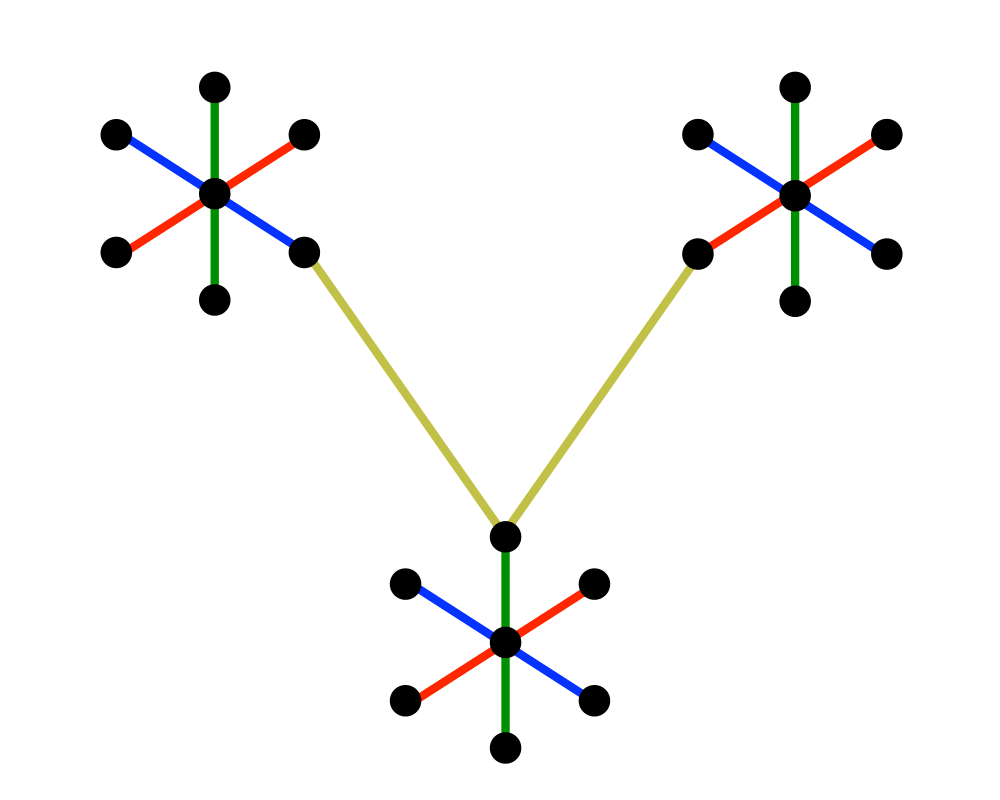 Minimum Spanning Tree |
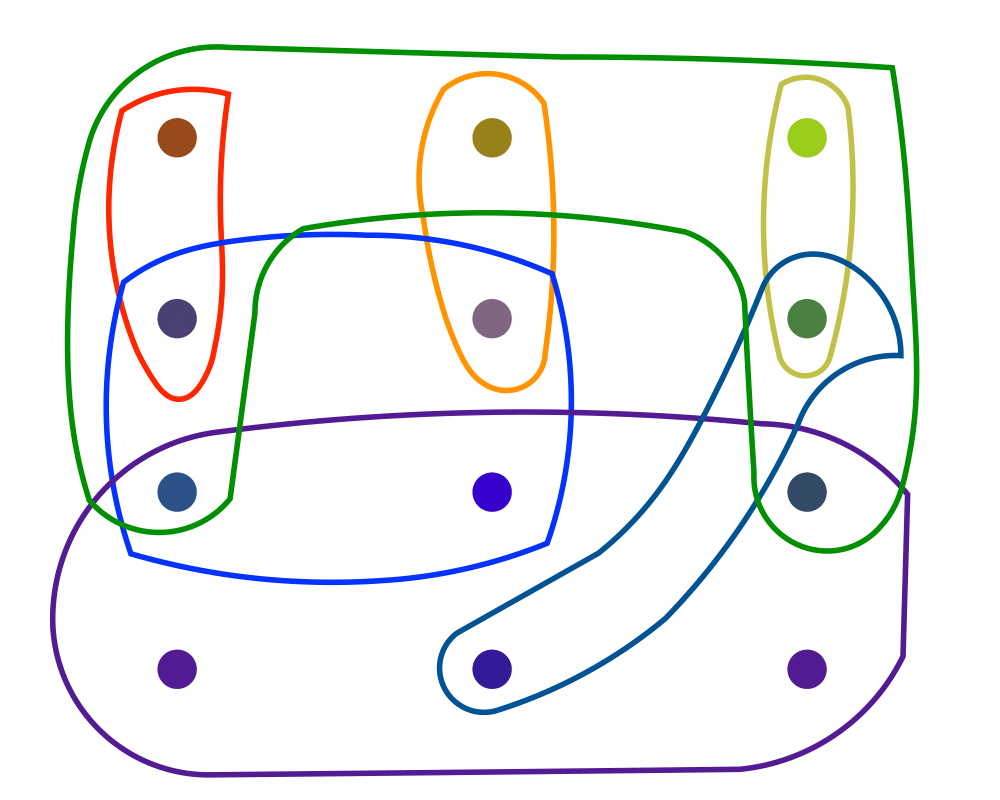 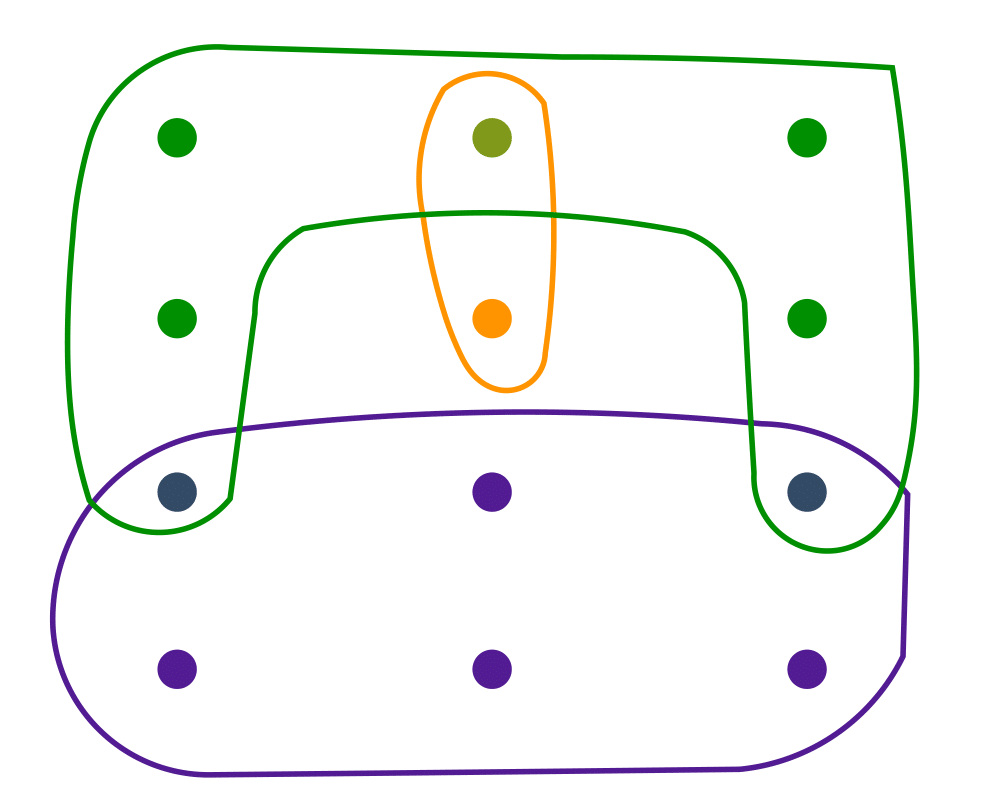 Set Cover |
As an Amazon affiliate, I earn from qualifying purchases if you buy from links on this website.